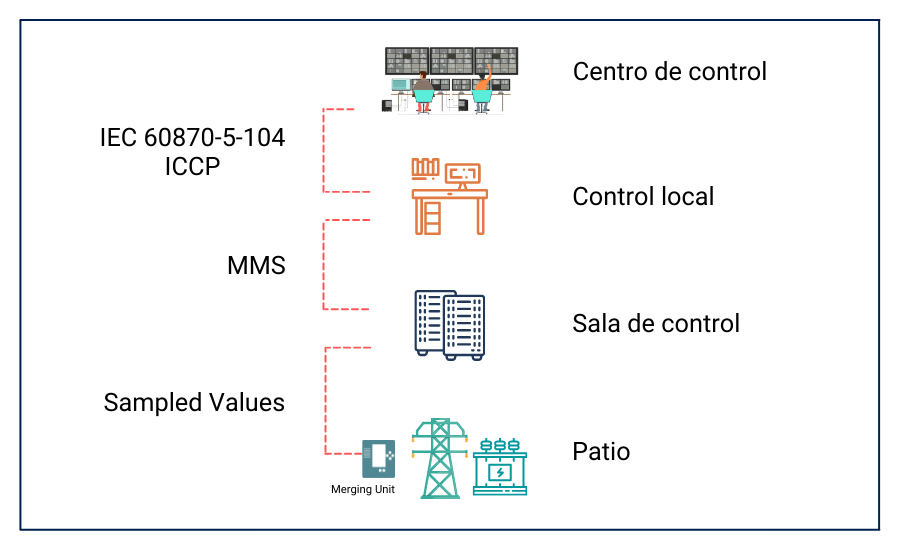
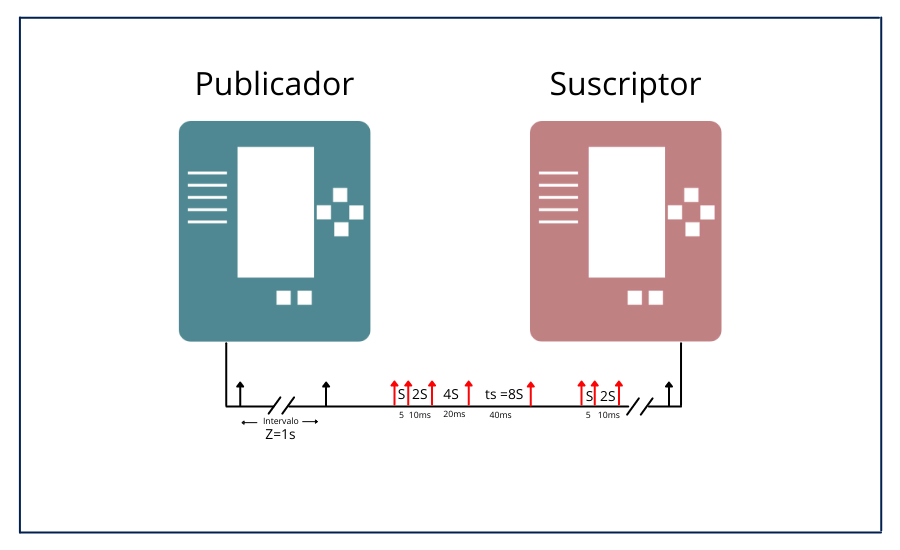
The IEC-61850 first version was published between 2001 and 2004. Since then, each part has been revised and extended towards a version 2 to content improve and respond to needs of others aspects in electric sector. In the first edition, standard’s authors published around 800 TISSUEs (Technical Issues) that generated comments and potential solutions to problems encountered. Table 1 present historical evolution summary each standard section showing list of changes pointed out by the IEC.
Part | Edition 1 | Edition2 | Main Changes |
Part 1: Introduction and overview | 2003 / 37 pp | 2013 / 73 pp |
|
Part 2: Glossary. | 2003/42pp |
|
|
Part 3: General Requirements. | 2002 / 33 pp | 2013 / 136 pp | Requirements are in line with other equipment used in same environment (e.g., protection relays)
|
Part 4: System and Project Management. | 2002 / 59 pp | 2011 / 74 pp | This second edition constitutes a technical revision to unify document with other IEC 61850 standard parts, in addition extending scope of substation automation systems to all used automation systems. |
Part 5: Communication requirements for functions and device models. | 2003 / 131 pp | 2013 / 306 pp |
|
Part 6: Configuration language for communication in electrical substations related to IEDs. | 2004 / 144 pp | 2009 / 215 pp |
|
Part 7.1: Basic communication structure – Principles and models | 2003 / 110 pp | 2011 / 289 | Information models for specific substation on automatic systems power.
|
Part 7.2: Basic communication structure – Abstract communication service interface (ACSI). | 2003 / 171 pp | 2010 / 213 pp | Some types of data not required have been removed.
|
Part 7.3: Basic communication structure – in electrical substations related to IEDs. | 2003 / 64 pp | 2010 / 182 pp | This second edition defines new common data classes used by new standards definition models objects based on IEC 61850 for statistical data representation and historical. |
Part 7.4: Basic communication structure in electrical substations related to IEDs – Common Data Classes. | 2003 / 104 pp | 2010 / 179 pp |
|
Part 8.1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Mappings to Manufacturing Message Specification MMS (ISO 9506-1 and ISO 9506-2) and to ISO/IEC 8802-3. | 2004 / 133 pp | 2011 / 386 pp |
|
Part 9.1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Sampled values over serial unidirectional multidrop point to point link. | 2003 / 29 pp | Replaced by: IEC 61850-9-2:2011 |
|
Part 9.2: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Sampled values over ISO/IEC 8802-3. | 2004 / 28 pp | 2011 / 65 pp | Adding link layer redundancy
|
Part 10: Conformance Testing. | 2005 / 43 pp | 2012 / 170 pp |
|
According these matters are corrections, clarifications, new functionality and the Elimination of features obsolete, others aspects such as:
- Added new sections parts such as the IEC-61850-80-1: a guide for information exchange from model Common Data Class Objects (CDC) using IEC 60870-5-101 or IEC 60870-5-104; In addition to models devices for Hydro-electric, Wind, Distributed Energy Resource and Power Quality.
- Object name longitude change from 64 to 128 characters.
- Logical Device hierarchy allowed.
- Extended SCL use to allow design bottom-up systems and multiple projects. The extensions are assigned. IID (Instantiated IED Description) and. SSD (System Specification Description).
- Added “tracking service” that replaces changes monitoring in outputs.
- Defined redundant system communication, where it is suggested HSR and PRP (Parallel Redundancy Protocol) Protocol (High-availability Seamless Redundancy).
- Improvements testing aspects for customers and sampled-values configuration language processors. Allowed to define a test mode for a function through the object Logical Mod Node LLN0. With “TEST-BLOCKED” mode help, function inputs are processed but result does not spread by physical outputs.
- Safety mechanisms definition.
- Mechanisms definition for declaring Multicast information subscribers (GOOSE and Sampled Values).
- Rename standard replacing “substation” by “system” to cover further aspects of substation.
- Erase IEC GSSE.
- Defined named enums independent whole counters.
- Added data types and data objects multiples.
Compatibility between versions 1 and 2 was a very important aspect considered. The most basic requirement is the ability to identify version in particular supported devices. In addition, it was necessary to consider environments where merge servers of each version. For communications, there are no major inconveniences. Some ambiguities related to buffered reports were solved. For models, the new version relates to new functionality. If a device supports this new functionality, public on version 2, while an equivalent process for access to this function is performed by a client. Same consideration applies to design tools.
In conclusion, version 2 IEC-61850 Standard Edition improves and wide-ranging features of version 1. These improvements include tests aspects, new functions inclusion and objects types used in modeling of electrical systems. It is compatible with version 1, even up to different versions servers in the same environment can co-exist.
Descarga nuestro simulador IEC 61850
Written by: PhD. Iván Dario Claros, Gerente R&D – Axon Group